キーワード: 極限量子計測、走査プローブ顕微鏡、量子光学、量子生命、量子機能
https://dora.bk.tsukuba.ac.jp/eqmqbs/index.html
 ナノスケールの科学技術は、分野間の垣根を超えた知見や個々のニーズの共有に基づいて進展してきました。
ナノスケールの科学技術は、分野間の垣根を超えた知見や個々のニーズの共有に基づいて進展してきました。
極限量子計測・量子生命・リサーチユニットでは、物理工学域を中心とした計測技術開発に携わる研究者による走査トンネル顕微鏡(STM)の技術開発を核として、量子素子開発や生命・医学分野の研究者と連携し、量子光学などの異なる分野の先端技術を融合した研究を行っています。これにより、新規量子素子の開発や、従来の技術では見ることのできなかった生命現象の解明、新しい医療技術の開発等の量子生命科学への展開を目指しています。
超微・超高速の現象を計測する極限計測法の開発
私たちはこれまで、走査トンネル顕微鏡(STM)と超短パルスレーザー技術を融合することにより、原子レベルの空間分解能と、フェムト秒(千兆分の1秒)レベルの時間分解能で超微・超高速の現象を計測できる新たな技術の開発を進め、世界に先駆けて局所スピンの超高速ダイナミクスの計測などを可能にしてきました。
STMの原理を簡単に言うと、先端の尖った金属の探針で物質の表面の形をなぞることにより、物質の形状を明らかにするものです。これを極小の世界で行うことで、原子一つ一つの並びを計測することができます。このSTM技術と、非常に短い時間だけ光る超短パルスレーザーを組み合わせることで、超微・超高速の現象を計測することができるようになりました。

図1:走査トンネル顕微鏡(STM)
量子素子開発や生命・医学分野の研究者と連携し、新たな学術領域の創出へ
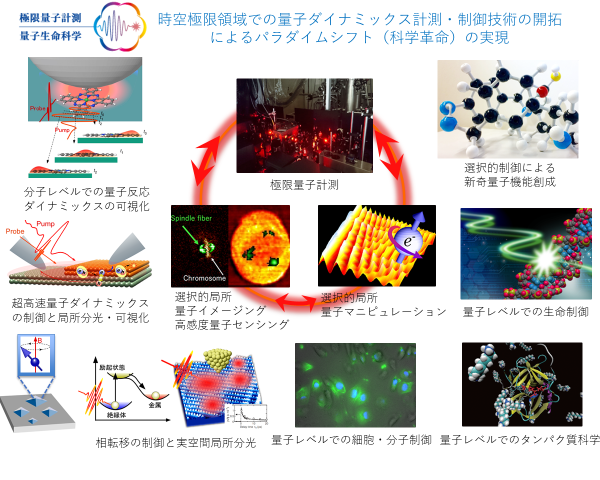
図2:時空極限領域での量子ダイナミックス計測・制御技術の開拓によるパラダイムシフト(科学革命)の実現
物理工学域を中心とした計測技術開発においては、半導体などの無機材料を主な研究対象としてきましたが、現在、量子素子開発や生命・医学分野の研究者と連携し、細胞などの生体材料を対象とした研究を展開しています。この連携は双方に学術的なメリットをもたらしています。
たとえば、癌のメカニズムを分子レベルで解明する研究では、物理工学域の研究者は医学領域の研究者から提供される細胞などの新たな研究対象を得る一方、医学領域の研究者は物理工学域の研究者から提供される技術によって今まで観測することができなかった原子レベルの現象を解明できます。
これまでの医学領域の研究が比較的マクロなスケールで行われており、分子内部の局所構造まで観測することが難しかったことや、分子を集団としてしか観測できなかったことを考慮すると、分子内部の原子レベルの現象を観測したり、個々の分子のふるまいを観測したりすることが可能になる私たちの研究は、医療分野に対し今までになかった知見を提供できると考えられます。
学際的な研究と多様な測定対象により、分子マシンや触媒、薬剤開発などの幅広い応用が開拓できるとともに、新しい学術領域の創出が期待されています。
社会への貢献・実績
- 科学研究費特別推進研究獲得(2017年)
- アメリカ物理学会(APS)動画放映(2018年)
- プレ戦略イニシアティブへの展開(20118年)
- JST-CREST獲得(2018年)
- 未来社会創造事業への採択
生細胞の分子機能をとらえる量子顕微鏡の開発(2019年) - JST-NexTEP採択
時間・スピン分解走査マルチプローブ顕微鏡の開発・株ユニソクとの共同事業(2019年)
取材日:2020年2月14日
Aiming at expansion to create novel quantum devices and drug discovery by developing cross-sectoral extreme metrology technology
Unit members : Matsui, Hirofumi Yoshida, Shoji
Other agencies : Oshima, Ryuji Mera, Yutaka Komiyama, Makoto Takagi, Satoshi Fujimoto, Kaoru
Unit name: Extreme Quantum Metrology & Quantum BioScience
Key words: Extreme Quantum Metrology, Scanning Probe Microscopy, Quantum Optics, BioScience, Quntum Function
https://dora.bk.tsukuba.ac.jp/eqmqbs/english/index.html

Nanoscale scientific technology has advanced based on knowledge crossing barriers among fields and sharing individual needs.
Extreme Quantum Metrology & Quantum BioScience Research Unit performs studies fusing advanced technologies of different fields, such as quantum optics, in cooperation with researchers of the quantum device development, life, and medical fields with a core of technology development of scanning tunneling microscope (STM) by researchers engaged in measurement technology development centering on the physical engineering field. Based on these achievements this Research Unit aims, for example, to develop novel quantum devices and quantum bioscience not able to be realized by conventional technologies.
Development of extreme metrology method measuring supermicro ultra-high-speed phenomena
We have progressed development of new technology capable of measuring supermicro ultra-high speed phenomena at atomic-level spatial resolution and femtosecond (one in quadrillion second)-level temporal resolution by fusing technologies of scanning tunneling microscope (STM) and ultrashort pulse laser and enabled significant measurements, including the ultra-high speed dynamics of local spin, first in the world.
Briefly, the principle of STM is to clarify the shape of materials by tracing the surface shape of the materials with a metal probe with a pointed tip. Performing this in a minimum world, alignment of each atom can be measured. By combining this STM technology and ultrashort pulse laser flashing for a very short time, measurement of supermicro ultra-high-speed phenomena became possible.

Fig. 1: Scanning tunneling microscope (STM)
Creation of a new academic field in cooperation with researchers of quantum device development, life, and medical fields
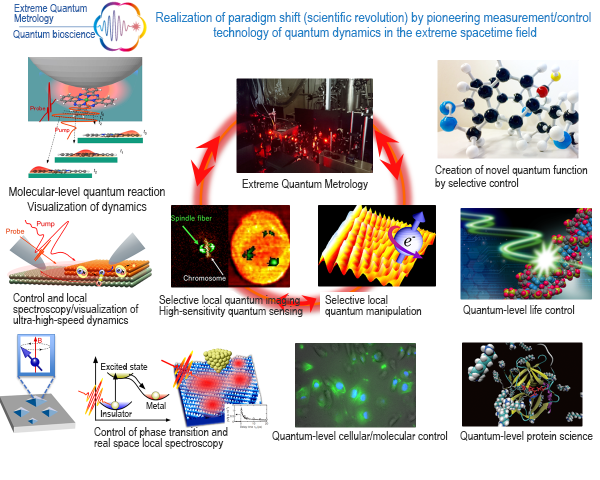
Fig. 2: Realization of paradigm shift (scientific revolution) by pioneering measurement/control technology of quantum dynamics in the extreme spacetime field
In measurement technology development centering on the physical engineering field, the main research subject was inorganic materials, such as semiconductors, but at present, we are performing studies targeting biological materials, such as cells, in cooperation with researchers of the quantum device development, life, and medical fields. This cooperation brings academic merits on both sides.
For example, in a study elucidating the cancer mechanism at a molecular level, researchers of the physical engineering field acquire new study subjects provided by researchers of the medical field, such as cells, whereas researchers of the medical field can elucidate atomic-level phenomena previously unable to be observed using technology provided by researchers of the physical engineering field.
Considering that previous studies in the medical field were performed at a relatively macroscopic scale, observation of the local structure inside the molecule was difficult, and molecules could be observed only as a population, our studies enabling observing intramolecular phenomena at an atomic level and behavior of individual molecules may provide knowledge previously absent in the medical care field.
Through interdisciplinary studies and diverse measurement subjects, a wide range of applications, such as development of molecular machines, catalysts, and drugs, can be pioneered and creation of a new academic field can be expected.
Social contributions and achievements
- Acquisition of Grant-in-Aid for Specially Promoted Research (2017)
- Video televising at American Physical Society (APS)(2018)
- Expansion to pre-strategic initiative (2018)
- Acquisition of JST-CREST (2018)
- Adoption to JST Mirai Program
Development of quantum microscope capturing molecular function of living cells (2019) - Adoption to JST-NexTEP
Development of time- and spin-resolved multi-probe scanning tunneling microscope/joint project with UNISOKU Co., Ltd. (2019)
Interviewed on February 14, 2020
