他のメンバー : 高木 英樹 坂入 洋右 酒井 利信 真田 久 前田 清司 大藏 倫博 中田 由夫 長谷川 聖修 徳山 薫平 尾縣 貢 武田 文 麻見 直美 鈴木 健嗣
キーワード:身心統合、スポーツ科学、たくましい心、認知脳科学、軽運動
http://bamis.taiiku.tsukuba.ac.jp/
 リサーチユニット「BAMIS身心統合スポーツ科学」では、2010年に身心統合スポーツ科学研究(Body and Mind Integrated Science: BAMIS)プロジェクトをスタートしました。
リサーチユニット「BAMIS身心統合スポーツ科学」では、2010年に身心統合スポーツ科学研究(Body and Mind Integrated Science: BAMIS)プロジェクトをスタートしました。
心・技・体をトータルに捉え、人々が「活力」や「しなやかさ」を備えた身体と心を持つために、運動がいかにして貢献するかを科学的に研究し、「たくましい心(ストレスを乗り越え安定し、前向きに行動できる)」を創出する革新的な運動プログラムを開発しています(図1)。

「SPARTS」-スポーツと芸術の融合
ふと音楽が耳に入り、体が自然にリズムに合わせて動いてくる。「運動」というと継続が難しく感じてしまいますが、音楽と運動により気分を前向きにし、ムー ドチェンジャーとしての運動の側面を活かすことにより、脳が活性化します。本リサーチユニットでは運動を利用し心を元気にする事に焦点を当て、時間とス ペースを節約するプログラムを考えました。それが「SPARTS」プログラム*1です。現在、東日本大震災の被災地域の学校に導入されており、スペースが なく共有環境が少ない場所で、2分3分で音楽に乗って運動するリズム体操で全身を動かします。その内容は、武道や東洋的身体技法(動き、呼吸、意識)を盛 り込んでおり、幅広い世代の人が一緒に歌いながら楽しく運動できるプログラムです(図2)。

運動という嗜好品
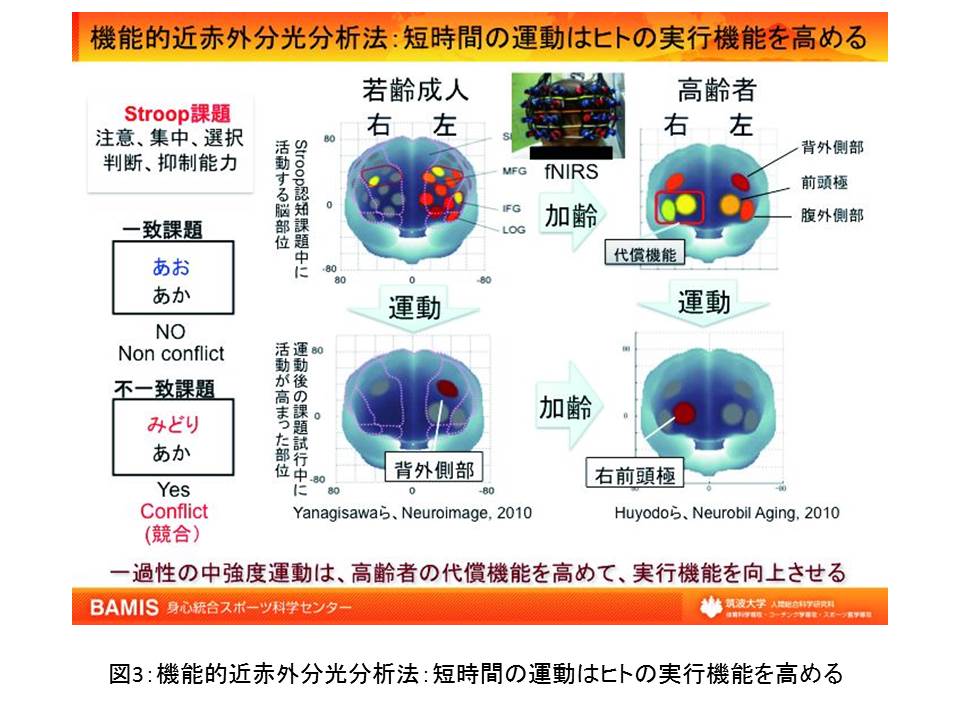
私たちは何気ない運動に光をあて、軽い運動でも楽しく行うことにより、体だけでなく、脳も活性化させ、認知機能を向上させることを解明しています(図 3)。これは健常人だけでなくうつ病の人にも、糖尿病の人にも有用できます。ちょっとした刺激・運動すると、適応原理すなわち生物原理が働き、筋肉も肥大 し、毛細血管やミトコンドリアも増えます。また、私たちの研究により、軽運動は脳の神経システムにおける成長因子を促進させることや、脳の海馬という記憶 や学習する器官において神経形成が起こる可能性があることが分かりました。
社会への貢献・実績
● 国際フォーラム(3回)、国内セミナー(37回)、国際シンポジウムを実施
● 研究内容がThe New York Timesの記事に掲載-記事名「Brains and Brawn」「How Exercise Fuels the Brain」「How Testosterone May Alter The Brain After Exercise」
● PNAS,Neuronに論文が掲載
● 韓国との国際的な研究者組織「KATS」の創設
● 文科省より復興教育支援の委託事業として東北各地の小学校にてSPARTSプログラムを実施
(取材:平成25年6月20日)
Scientific Innovation to Nurture Mental Strength: Body and Mind Integrated Science
Unit members : Takagi, Hideki Sakairi, Yosuke Sakai, Toshinobu Sanada, Hisashi Maeda, Seiji OKURA, Tomohiro Nakata, Yoshio Hasegawa, Kiyonao Tokuyama, Kunpei Ogata, Mitsugi Takeda, Fumi Omi, Naomi Suzuki, Kenji
Key words: integration of the body and mind, sport science, mental strength, cognitive and brain sciences, low-intensity exercise
This research unit, named: Body and Mind Integrated Science: BAMIS, launched the BAMIS Project in 2010, with a view to developing innovative exercise programs to nurture mental strength (to overcome  stress and perform stable and proactive behaviors) by scientifically examining the effects of exercises to maintain a vital and flexible body and mind, while simultaneously focusing on the physical, mental, and technical aspects (Figure 1).
stress and perform stable and proactive behaviors) by scientifically examining the effects of exercises to maintain a vital and flexible body and mind, while simultaneously focusing on the physical, mental, and technical aspects (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Body and Mind Integrated Science: BAMIS
“SPARTS” – A Combination of Sports and Arts
When you listen to music, your body naturally moves, getting into a rhythm. Doing “exercise” sounds difficult; however, in combination with music, it creates positive feelings, and activates your brain. This research unit has been engaged in the development of time- and space-saving exercise programs to refresh the mind, such as the SPARTS program*1, which has been adopted in schools affected by the Great East Japan Earthquake. This program is applicable even in limited spaces and shared environments, and is based on a 2- or 3-minute rhythmic exercise to move the entire body, while listening to music. Adopting martial arts and oriental physical techniques (motions, breathing methods, and mental concentration), it enables a wide range of age groups to enjoy time together, singing and moving (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Jump Exercise (SPARTS) at a Disaster-affected Elementary School
Pleasure-creating Exercise
Focusing on daily physical activities, we have demonstrated that it is possible to activate not only the body, but also the brain, and improve the cognitive function by performing enjoyable low-intensity exercise (Figure 3). In addition to healthy people, such exercise is also performable by those with depression or diabetes. With slight stimulation as exercise, the muscle mass and numbers of capillaries and mitochondria increase based on the principle of adaptation or as a biological response. Furthermore, our previous studies revealed that low-intensity exercise promotes growth factors in the central nervous system, and suggested the possibility of neurogenesis in the hippocampus as the organ responsible for memory and learning.

Figure 3: Functional Near-infrared Spectrophotometry: Short-term Exercise Promotes Executive Functioning
Social contributions and achievements
● Holding international forums (3), domestic seminars (37), and an international symposium
● Being introduced in the New York Times, with titles: “Brains and Brawn”, “How Exercise Fuels the Brain”, and “How Testosterone May Alter the Brain after Exercise”
● Publishing articles in the journals PNAS and Neuron
● Founding an international association of researchers, named KATS, in cooperation with Korea
● Implementing the SPARTS program in schools located in east Japan as a post-disaster support business entrusted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology
