キーワード: 神経活動、神経回路、脳機能、運動機能
http://www.md.tsukuba.ac.jp/basic-med/physiology/
 頭が良くなるためにはどうすれば良いか考えたことはありませんか?脳の中で一番大切なのは、脳のどこの領域とどこの領域が情報交換しているかという神経回路です。ドーパミンという神経伝達物質は、神経回路のつながりを強めたり、弱めたりする働きがあります。そのような働きは私たちの精神機能の維持に深く関係しています。神経生理学リサーチユニットの4つのグループの1つである認知行動神経行動学グループでは、ドーパミンに注目して、研究活動を行っており、国内外からの注目を集めています。
頭が良くなるためにはどうすれば良いか考えたことはありませんか?脳の中で一番大切なのは、脳のどこの領域とどこの領域が情報交換しているかという神経回路です。ドーパミンという神経伝達物質は、神経回路のつながりを強めたり、弱めたりする働きがあります。そのような働きは私たちの精神機能の維持に深く関係しています。神経生理学リサーチユニットの4つのグループの1つである認知行動神経行動学グループでは、ドーパミンに注目して、研究活動を行っており、国内外からの注目を集めています。
ドーパミンの認知機能の可能性
ドーパミン神経細胞から放出されるドーパミンは意欲や報酬に関わっているということはこれまでの研究からもわかっていました。パーキンソン病や鬱、ADHD、統合失調症にもドーパミン神経系の異常が関わると報告されており、患者さんは意欲障害の症状を示します。パーキンソン病の患者さんのその他の症状を見てみると、意欲障害だけではなく、認知機能障害、運動機能障害も併発しています。意欲障害はこれまでのドーパミンの研究で説明できます。しかし、なぜそれ以外の認知機能・運動機能障害がおきるのでしょうか?そこで私たちのグループではドーパミンの認知機能に関する役割に注目して研究をしています。
これまでとは違うドーパミン神経細胞の活動
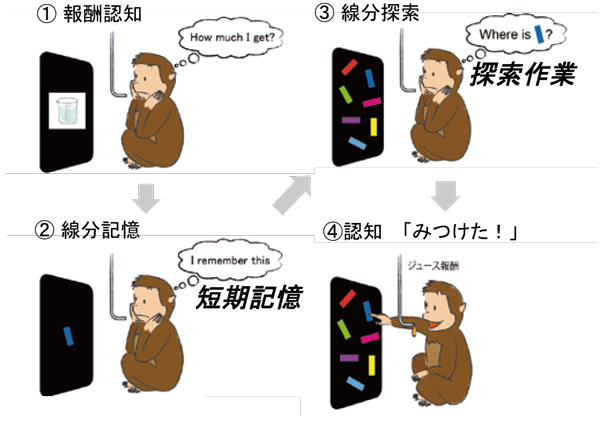
図1:サルに行わせた視覚探索課題
私たちのグループでは、脳構造が人間に比較的近い霊長類に様々な認知行動課題をおこなわせ、視覚探索課題を行わせた時の神経細胞の活動を調査しています。まず、モニターを使い、最初にどれくらい報酬(リンゴジュース)が与えられるかを示した後、ある線分を覚えさせます。その後一定のタイムラグ後にたくさんの線分を表示させ、その中から覚えた線分を選ばせます(図1)。するとドーパミン神経細胞は、線分を記憶する際に活動を上昇させました。また、「これだ」と正解の線分を見つけた時にも活動が上昇しました。一方、より簡単な探索条件(たとえばたくさんの○の中から△を見つけ出す条件)で正解を見つけても、ドーパミン神経細胞の活動の上昇がみられませんでした。このような結果から、ドーパミン神経細胞が記憶や視覚探索に係わる何らかのシグナル伝達に関わっていると考えられます。
このような活動を示すドーパミン神経細胞は、黒質緻密部と呼ばれる脳領域の一部で観察されました。これは、今まで報告されてきた意欲や報酬に関わるシグナルを伝達するドーパミン神経細胞の他に、認知機能に関わるシグナルを伝達するグループが存在することを示しています(図2)。私たちのグループはこのようにドーパミン神経細胞は認知機能に関してもなんらかの信号を出していると考えており、今後例えば、認知機能が高められるときに、ドーパミン神経細胞の活動が上昇するのであれば、その時にその活動を減弱あるいは増減させて、認知機能がどうなるのかという事が調べられるような実験をしていきます。
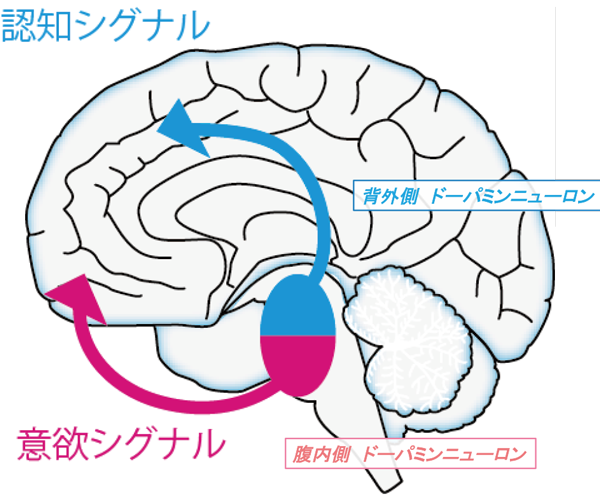
図2:2つの異なるドーパミンシグナル
社会への貢献・実績
- 2013 年 文部科学大臣表彰 若手科学者賞
- 2010 年 日本神経科学学会 奨励賞
- 2008 年 日本神経回路学会 論文賞
取材:平成27年5月14日
When thinking “I found it!” or “This is it!”, you have a chance to improve your brain function!
Unit name: Neurophysiology
neural activity, neural circuit, brain function, motor function
 Have you ever thought about ways to become smarter? In your brain, neural circuits for information exchange between brain areas are the most important for this. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that enhances or weakens connections in neural circuits. Such function is closely related to the maintenance of our mental function. The Cognitive and Behavioral Neuroscience Group, one of 4 groups that form the Neurophysiology Research Unit has performed research focusing on dopamine, and this group receives remarkable attention from Japan and other countries.
Have you ever thought about ways to become smarter? In your brain, neural circuits for information exchange between brain areas are the most important for this. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that enhances or weakens connections in neural circuits. Such function is closely related to the maintenance of our mental function. The Cognitive and Behavioral Neuroscience Group, one of 4 groups that form the Neurophysiology Research Unit has performed research focusing on dopamine, and this group receives remarkable attention from Japan and other countries.
The possibility of the involvement of dopamine in cognitive function
Previous studies have shown that dopamine released from dopamine neurons is involved in motivation and reward. In addition, abnormalities in the dopamine neuron system have been reported to be involved in Parkinson’s disease, ADHD, and schizophrenia. Patients with these disorders associate with motivational impairment. In patients with Parkinson’s disease, not only motivational impairment but also cognitive and motor impairments are observed. Previous studies on dopamine can explain how motivational impairment occurs. However, why do cognitive and motor impairments also occur in patients with Parkinson’s disease? Thus, our group has studied the role of dopamine in cognitive function.
Dopamine neuron activity differing from that previously reported
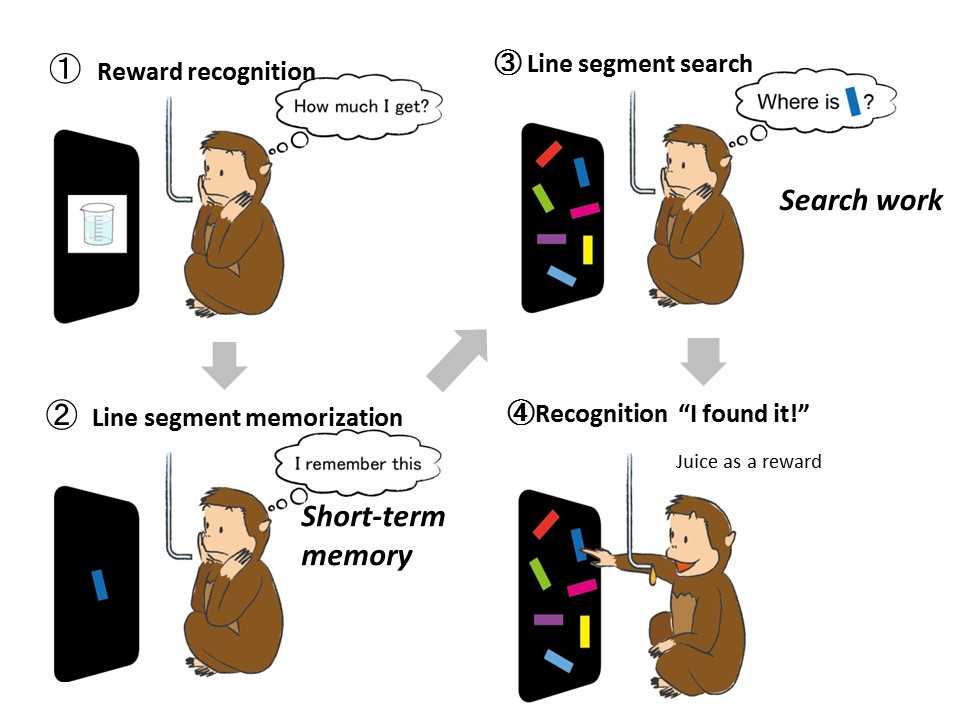
Fig. 1: The visual search task given to monkeys
Our group gave various cognitive behavioral tasks to primates, whose brain structure is relatively close to that of humans, and investigated neuron activity during visual search tasks. After the amount of a reward (apple juice) was shown on a monitor, a certain line segment was shown to monkeys for memorization. After a certain time-lag, many different line segments were shown, and monkeys were instructed to locate the memorized line segment (Fig. 1). Our group found that the activity of dopamine neurons was increased when monkeys memorized the line segment as well as when found the correct line segment (“This is it!”). However, the dopamine neuron activity was not increased even when the correct answer was found under more straightforward search conditions such as finding a triangle (D) among many circles (○). These results suggest the involvement of dopamine neuron in the transmission of certain signals associated with memory and visual search.
Dopamine neural cells showing such activity were observed in a part of the brain area called the substantia nigra pars compacta. This suggests the presence of a dopamine neuron group that transmits signals related to cognitive function in addition to previously reported dopamine neurons that transmit signals related to motivation and reward (Fig. 2). Our group hypothesizes that the dopamine neuron also transmits certain signals related to cognitive function. In the future, if dopamine neuron activity is evaluated during increased cognitive function, we intend to perform studies in which the dopamine neuron activity is reduced or increased during increased cognitive function, and changes in cognitive function are evaluated.
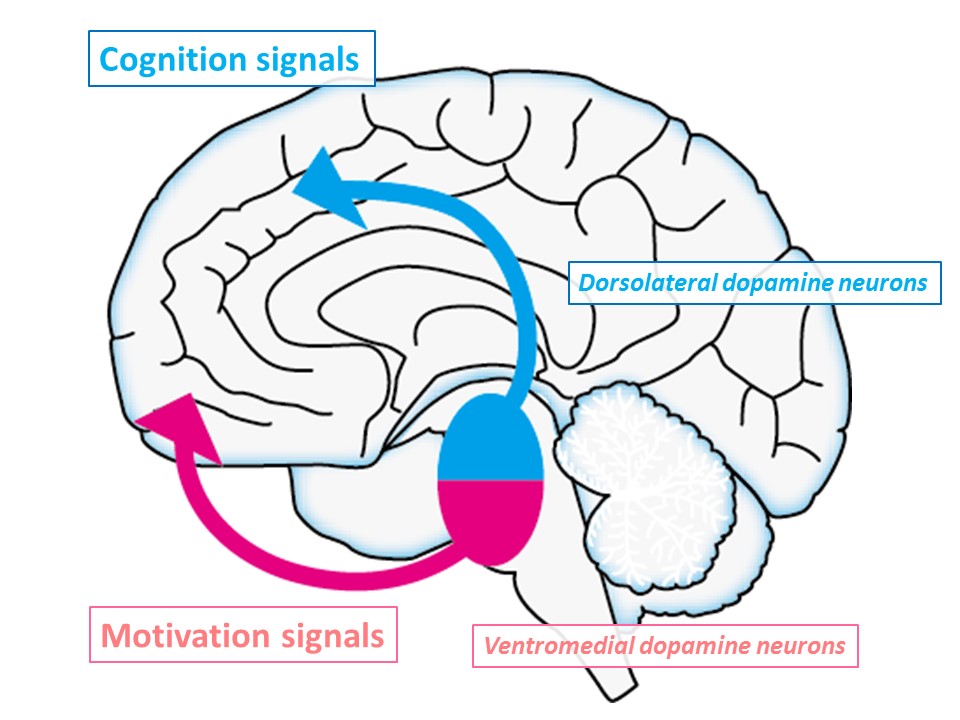
Fig. 2: Two different dopamine signals
Social contributions and achievements
- 2013, The Young Scientists’ Prize, The Commendation for Science and Technology by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 2010, Young Investigator Award, The Japan Neuroscience Society
- 2008, Original Paper Award, The Japanese Neural Network Society
Interviewed on May 14, 2015
